
- 1.800.834.8669
- LIVE Chat Support
You have no items in your shopping cart.
LED vs Halogen Headlights - Which Bulb is Better?
Comparing halogen and LED headlights. Are LEDs better than halogens? Which should you choose and why.
Last updated: August 29, 2023
Halogen vs LED Headlights
LED and halogen are two types of bulbs. Most vehicles on the road still use halogens, however, newer vehicles are increasingly being produced with the latest headlight bulb technology, LED.
The main difference between halogen and LED headlights is that halogen bulbs use a tungsten filament that heats up to produce light (incandescence), while LED headlight bulbs generate light through a diode (electroluminescence).
So, which is better? Compared to halogens, LEDs are better because they are:
- 300% brighter
- Last 6 times longer
- Use 85% less energy
- Emit very little heat
These important advantages over halogens explain why so many drivers and car manufacturers are looking to upgrade their headlight bulbs to LED.
LED Headlights vs Halogen Comparison Table
Here's a summary of the key differences between halogen and LED headlight bulbs.
| LED | Halogen | |
| Brightness | Very Bright (9,000 lumens) | Dull (3,000 lumens) |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Low |
| Power Draw | Low | High |
| Lifespan | 12,000 hours + | 2,000 hours |
| Light Distance | 985 ft | 325 ft |
| Heat Emission | Low | High |
| Price | $90 - $200 | $20 to $80 |
| Light Color | Bright white | Yellow |
| Warm-Up Time | No | Yes |
| Installation Time | About 30 mins | About 30 mins |
Halogen vs LED Headlights with Pictures
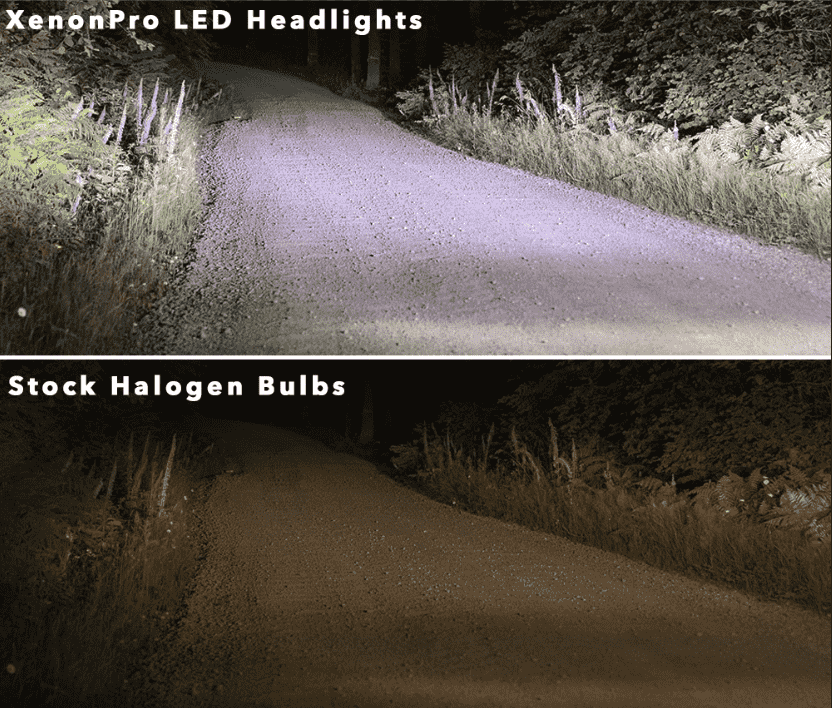
Brightness
When it comes to brightness, LED headlights are significantly brighter than halogens. This is the result of their superior technology and the bright white color they emit compared to halogens.
As you can see below, halogen headlights produce a dull and yellow beam, making it difficult to see well at night.

Since LEDs are more powerful, they not only produce a dense beam with no dark spots but they also illuminate a longer distance and wider area.
Distance
An important consideration for headlight bulbs is how much distance and area is covered by the light beam and rightfully so.
LEDs can reach a distance of up to 985 feet (300 meters) compared to halogens which can hardly cover 325 feet (100 meters).
LEDs cover a wider range, illuminating the sides of the road better while getting rid of those dark spots.

Power Consumption (Energy Efficiency)
One main advantage of LEDs over halogen headlights is that they are extremely energy efficient. They can produce significantly more light using a fraction of the energy consumed by halogens.
As a more energy-efficient bulb, LEDs draw less power from a vehicle and emit less heat inside the headlight assembly, which helps explain their long lifespan.
Lifespan
LED headlight bulbs can easily last 3 to 10 years compared to halogen bulbs that typically last 6 to 9 months. That's a huge difference.
Halogens have such a short lifespan because they're prone to failure by design. Halogens create light by heating the tungsten filament but that in turn creates heat that makes the tungsten evaporate. With time, the filament becomes too thin to produce light or simply breaks.
LEDs, on the other hand, burn out when the semiconductor material (the yellow part of the bulbs) degrades to the point that it can longer produce light. This can easily take 3+ years in high-quality bulbs.
In brief, the diodes on LED bulbs are significantly more resilient than the tungsten in halogens.
Price
LED headlight bulbs are more expensive than halogens on a per-bulb basis, however, LED is significantly cheaper over a long period since they last so long.
Let's take a simple example where LEDs cost $10 and halogens $5. At first glance, halogens appear to be 50% cheaper - an important difference.
However, if LEDs last 3 years while halogens only last 6 months, you'll be spending $10 in total on LEDs and a whopping $30 on halogens over 3 years.
That's 300% more spent on halogens than LEDs!
Choosing Between LED and Halogens
Who should use halogens? If you ask us, nobody should use halogen headlight bulbs. Overall, they are terrible compared to their LED or HID headlight counterparts and need to be changed frequently.
If you do not drive a lot, live and spend the vast majority of your time in a place where the streets are always very well illuminated, if you have a limited budget, or if you are simply satisfied with the current light output of your car, then halogen bulbs should be fine for you.
If you are an active driver, drive often at night, live out in the country, go out in the woods often and/or simply want to improve your vehicle’s light output and get that luxury look from your headlights, upgrading to LED headlights is ideal for you.
Whether you are considering buying a car with stock LEDs, looking to purchase the LED option for your new car, retrofitting your headlight assembly, or converting your existing halogen assembly to LED, we can assure you that you won’t regret your decision.
Upgrading From Halogen To LED Headlights
If you’ve read this far, you must be very interested in finally making the switch over to LEDs, and rightfully so.
If your car, truck, SUV, motorcycle, ATV, or snowmobile is currently equipped with halogen bulbs, you can easily swap them out with LEDs.
They are incredibly easy to install and will make a noticeable difference in your nighttime driving experience while making your vehicle look modern.
Different Types of Vehicles
The facts above apply to all vehicle types. Whether you drive a car, truck, motorcycle, snowmobile, ATV, camper, motorhome, or tractor, LEDs will be better and brighter than halogens.
Projector Headlights
One interesting thing about LEDs is that they have a tendency of performing poorly in projection headlights.
The science behind is not clear but in some cases, halogens might produce more light than LEDs. For these types of headlight assemblies, we always recommend HID headlight bulbs.
You can learn more about this topic here.
Technology
Halogen Headlight Bulbs
Halogen bulbs are one of the first and oldest lighting technologies used in cars as far back as the 1960s and were commercialized in North America around 1983.
The vast majority of cars and trucks come equipped with halogen bulbs because they are cheap, provide sufficient light as required by transport authorities, and newer technologies such as LED and HID headlights are not yet widespread.
Without getting too technical, halogen headlight bulbs essentially generate light by heating a metal filament (tungsten) inside the bulb. Halogen gas (Iodine and Bromine) is contained within the bulb to improve lifespan and improve brightness through what is known as a halogen cycle.
As a consequence of its heat-focused design, halogen bulbs are highly inefficient, do not last very long, give off a dull yellowish color, and emit a ton of heat. It is estimated that over 85% of the total power consumed is wasted as infrared heat, while under 15% goes to produce light.
LED Headlight Bulbs
LED bulbs are the latest development in the lighting industry and quickly gaining popularity among drivers. As mentioned briefly above, LED headlight bulbs are incredibly bright yet consume very little power, emit close to no heat, and last over 10 times longer than halogens.
Drivers want to see better, drive safer, and spend as little money and time as possible maintaining/replacing their headlight bulbs.
As a result and due to growing demand, we are seeing more and more cars coming with LED headlights or at least with an upgrade option from Fords and Kias to Audis and Bentleys.
To keep things simple, LED (light-emitting diodes) headlight bulbs generate light by passing electricity through a diode, a type of semiconductor that emits light when powered.
As a result of this advanced technological design, LED bulbs are incredibly efficient at turning electricity into light leading to very little waste, requiring less power, and emitting close to no heat.
The diode-based technology also allows for every LED bulb color temperature, unlike halogen which is restricted to yellow and yellowish-white.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Yes. LED bulbs are 6 to 10 times brighter than halogen. For example, drawing approximately 20 watts of power will produce ~2400 lumens with LED and only ~400 with halogens.
LED headlights are better than halogen for many reasons. LED bulbs are brighter, last longer, consume less energy, and emit less heat than halogens.
Yes. LED bulbs will consume 75% to 85% less energy than halogen bulbs to produce the same amount of light. For example, to produce approximately 2000 lumens of light, LEDs will draw ~20 watts while halogens will draw ~125 watts.
Yes, but using halogen bulbs is more expensive over time. When simply comparing the cost of the bulbs, LED bulbs can be up to 30% more expensive. However, considering that they last a lot longer and consume significantly less power, LEDs are in fact up to 50% cheaper than halogens.
Yes. LED headlight bulbs can last up to 45,000 hours, up to 10 times longer than halogen bulbs.
Yes, halogen headlight bulbs (55w) heat up to approximately 150 degrees while LED headlight bulbs heat up to under 90 degrees.
LED headlight bulbs convert the vast majority of the energy drawn into light (up to 90%) and therefore emit little heat. Halogen bulbs, on the other hand, convert over 85% of their energy into heat and less than 15% into actual light.
Sources:
- XenonPro.com Research
- Halogen Lamps - How They Work & History - Edison Tech Center
- Learn About LED Lighting - Energy Star
Disclaimer: The information contained on this page is provided free of charge to our visitors. It was prepared to the best of our abilities and with all the information available to us at the time of writing. We reserve the right to change, remove, or update any information contained on this page at any time and without notice to improve its accuracy. The most reliable method to determine the bulb size is by pulling your actual bulb(s) and reading the part number indicated directly on the bulb. The information compiled on this page comes with no guarantees or warranties.






















